
The study
Collaboration is coded into the project’s DNA. Inter-disciplinary and inter-institutional, it draws on cardiovascular biologists, immunologists, clinical cardiologists and experts in cardiac imaging from 13 organisations and multiple partner organisations across Europe.

The context
Cardiovascular diseases are a major cause of illness and death worldwide. Despite treatment advances for heart attacks (medically referred to as myocardial infarction, or MI), their occurrence still results in up to 50% of patients developing dysfunction in one of the heart’s main pumping chambers – namely, the left ventricle. This is critical given that left ventricular dysfunction is the strongest predictor of a poor outcome following heart attack, indicating 3 to 4-times mortality risk.

Objectives
The overall aim is to repurpose an existing drug, rituximab, to target the body’s immune response following a very serious type of heart attack – known as STEMI (ST elevation myocardial infarction) – and assess the drug’s impact on subsequent recovery of heart function.
To support this aim, the study includes a primary objective :
- prove the core concept that the drug can improve heart function in STEMI patients
plus a few secondary objectives :
- assess the impact of the drug on vascular inflammation (using 18F-FDG-PET/CT)
- better understand the immunopharmacology and cardioprotective mechanisms of rituximab
Myocardial infarction (MI) – A heart attack.
STEMI – acute ST elevation myocardial infarction, a very serious type of heart attack.

Concept
The study’s central idea is that B lymphocyte cell depletion, brought about using rituximab in patients with acute STEMI, will limit the amount of dead tissue (the infarct size) and the swelling of the heart muscle (cardiovascular inflammation) caused by the heart attack, and improve the heart’s recovery and function. An additional hypothesis is that the therapy will tame the excessive inflammatory response and the accelerated thickening of the artery walls (atherosclerosis) after such heart attacks.
Members of the RITA MI 2 inter-disciplinary consortium have previously shown that mature B cells are instrumental in coordinating a detrimental inflammatory response after cardiac injury resulting from reduced blood supply (myocardial ischaemia). This led to the current idea of targeting selective immune pathways, with an available drug, to deplete B cells and hopefully bring about significant cardiovascular protection and improved outcomes for patients with serious coronary artery disease.
Getting technical
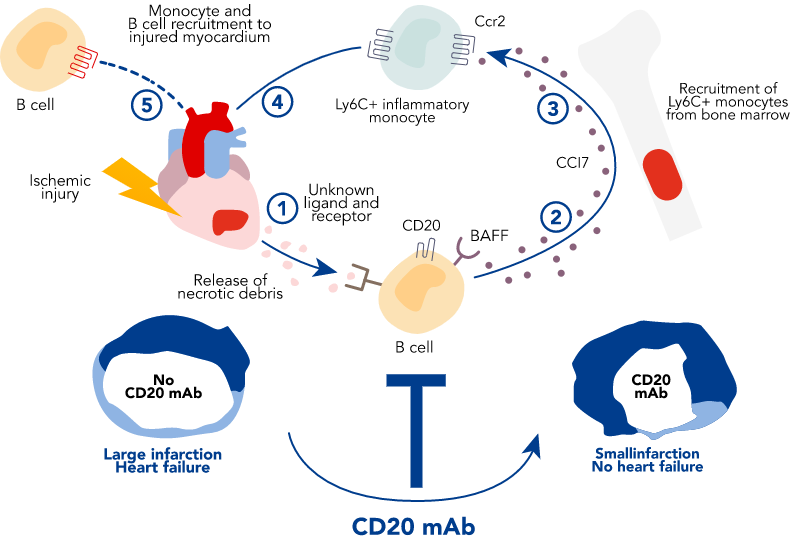
Myocardial damage after a heart attack (1) activates immune receptors on B lymphocytes (2), which leads to the production of inflammatory mediators, like CCL7 (3). CCL7 then activates its receptor CCR2 to mobilise inflammatory monocytes from the bone marrow to the blood and to the damaged heart (4). Excessive recruitment of inflammatory monocytes leads to adverse cardiac remodelling (5).
Achieving B cell depletion, via CD20 mAb rituximab, limits ischaemia-induced myocardial inflammation, reduces infarct size and improves heart function.
B lymphocyte cell – Part of the immune system, a type of white blood cell that makes antibodies.

Methodology
This state-of-the-art study uses the best scientific and clinical methods, equipment and environments available. As with all quality clinical drug research, the study will be double-blind and placebo-controlled.
Equal cohorts of around 190 STEMI sufferers – specifically acute anterior STEMI – will be randomly given one infusion of 200 mg of rituximab, or 1000 mg of rituximab, or else placebo. All participants will receive a recommended pre-medication of methylprednisolone to reduce potential side effects related to drug infusion.
The main measure of the treatment’s success (the primary endpoint) will be the amount of blood being pumped from the heart’s left ventricle with each heartbeat, using a measure known as left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), at 6 months after treatment – measured using cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR).
Several other trial endpoints will also be measured, including vascular inflammation (using 18F-FDG-PET/CT), the assessment of the amount of dead tissue, or infarct size (using CMR), and various biological markers.
Left ventricle – 1 of 4 heart chambers, the one that pumps blood round the body.
Beyond state-of-the-art

The research is unique, going beyond current understanding in the field because :
It targets a novel, highly relevant inflammatory pathway that orchestrates the adverse cardiac remodelling after heart attack
The same inflammatory pathway plays a detrimental role in the acceleration of atherosclerosis
after a heart attack. The treatment strategy therefore constitutes a double-hit approach
It’s a simple yet potentially very effective ‘fire-and-forget’
approach, requiring a single drug infusion after a heart attack

Work packages
The study is subdivided into interlocking work packages to maintain effective focus across distinct project activities. Different aspects are delegated to the team(s) best suited to perform and monitor those tasks.
WP1 : Project management & coordination
Staying on track, on budget, on time.
WP2 : Clinical study sponsorship
Coordinating activities and monitoring progress.
WP3 : Organisation, conduct, data & statistics
Staying in accordance with Good Clinical Practice.
WP4 : Assessment of heart function & inflammation
Imaging of cardiac function and remodelling (use CMR) and vascular inflammation (use PET/CT).
WP5 : Immunophenotyping & cardiovascular biomarkers
Assess circulating B cells, cytokines, cardio-biomarkers. Conduct blood immunophenotyping.
WP6 : Dissemination, exploitation and innovation management
Communicate results, manage intellectual property, prepare for phase 3.
